Have you ever wondered about the potential risks of being exposed to Penicillium mold? In this article, we will explore the symptoms that can arise from such exposure and shed light on the potential dangers. Whether you are concerned about the health implications or simply curious, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the symptoms of Penicillium mold exposure and help you understand the potential risks involved. So, let’s dive right in and uncover the facts!
Understanding Penicillium Mold
Penicillium mold is a type of fungus that belongs to the genus Penicillium. It is commonly found in indoor and outdoor environments and can cause a range of health issues for those who are exposed to it. In this article, we will explore what exactly Penicillium mold is, where it is commonly found, the different types of Penicillium mold, the health risks associated with exposure, and the factors that contribute to its growth.
What is Penicillium Mold?
Penicillium mold is a common type of fungus that can be found in a variety of environments, including soil, decaying matter, and indoor spaces. It is characterized by its fuzzy or powdery appearance and typically appears in shades of blue, green, or white. Penicillium mold reproduces by releasing spores into the air, which can easily spread and contaminate nearby surfaces.
Where is Penicillium Mold Found?
Penicillium mold can be found in a wide range of environments, both indoors and outdoors. Indoors, it can often be found in buildings with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms, kitchens, or basements. It can also grow on damp or water-damaged surfaces, such as walls, ceilings, and carpets. Outdoors, Penicillium mold can be found in soil, decaying vegetation, and on fruits and vegetables.
Common Types of Penicillium Mold
There are over 300 recognized species of Penicillium mold, each with its own unique characteristics and preferences for growth conditions. Some of the most common types of Penicillium mold include Penicillium chrysogenum, Penicillium notatum, Penicillium italicum, and Penicillium expansum. Each of these types can vary in color, texture, and potential health risks.
Health Risks Associated with Penicillium Mold
Exposure to Penicillium mold can pose various health risks, particularly for individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing respiratory conditions. The spores released by Penicillium mold can cause allergic reactions, trigger asthma attacks, and even lead to potentially serious infections in some cases. It is important to be aware of the potential health risks and take appropriate measures to prevent exposure.
Factors Contributing to Penicillium Mold Growth
Several factors can contribute to the growth and proliferation of Penicillium mold. Moisture and humidity play a significant role in its development, as Penicillium mold thrives in damp environments. Poor ventilation can also contribute to the growth of Penicillium mold, as it inhibits the circulation of fresh air and allows moisture to accumulate. Additionally, water leaks, condensation, and water damage can create ideal conditions for Penicillium mold to grow.
Signs and Symptoms of Penicillium Mold Exposure
Exposure to Penicillium mold can lead to a variety of signs and symptoms, which can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the extent of exposure. Here are some common symptoms associated with Penicillium mold exposure:
Respiratory Symptoms
One of the most common symptoms of Penicillium mold exposure is respiratory distress. This can manifest as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions may experience an exacerbation of their symptoms.
Allergic Reactions
Penicillium mold can also trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. These reactions can vary in severity and may include nasal congestion, sneezing, itching, watery eyes, and a runny or stuffy nose. In more severe cases, individuals may experience hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
Skin Symptoms
Exposure to Penicillium mold can cause skin symptoms in some individuals. These symptoms may include redness, itching, rash, and irritation. In rare cases, prolonged contact with Penicillium mold may even lead to fungal skin infections.
Eye and Sinus Symptoms
Some individuals exposed to Penicillium mold may experience eye and sinus symptoms. These can include redness, itching, watering of the eyes, sinus congestion, and sinus headaches. In more severe cases, individuals may develop sinus infections or other sinus-related complications.

Complications and Long-term Effects
Exposure to Penicillium mold can sometimes lead to complications and long-term effects, particularly in individuals with underlying health conditions. Here are some potential complications associated with Penicillium mold exposure:
Asthma and Respiratory Disorders
For individuals with asthma, exposure to Penicillium mold can worsen symptoms and may even lead to the development of asthma if they are not already diagnosed. Prolonged exposure to Penicillium mold can also increase the risk of developing other respiratory disorders, such as chronic bronchitis or allergic alveolitis.
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
In some cases, individuals exposed to Penicillium mold may develop a severe allergic reaction known as Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA). This condition is characterized by inflammation and allergic response in the lungs, which can cause persistent coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS)
Exposure to Penicillium mold can also lead to the development of Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS) in some individuals. AFS is a condition characterized by chronic inflammation and fungal infection in the sinuses, leading to symptoms such as persistent nasal congestion, facial pain, and nasal discharge.
Invasive Aspergillosis
Although rare, prolonged exposure to Penicillium mold can sometimes lead to the development of invasive aspergillosis. This is a serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infection that primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems. Invasive aspergillosis can affect various organs in the body, including the lungs, brain, heart, and kidneys.
Other Infections and Health Conditions
In addition to the conditions mentioned above, Penicillium mold exposure can also increase the risk of other infections and health conditions. This can include respiratory infections, sinus infections, fungal skin infections, and exacerbation of existing respiratory conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect that you have been exposed to Penicillium mold and are experiencing symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some steps that may be involved in the diagnosis and treatment process:
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the initial consultation, your healthcare provider will likely ask about your medical history, including any pre-existing respiratory conditions or allergies. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your symptoms and determine the potential cause.
Mold Testing and Analysis
If mold exposure is suspected, your healthcare provider may recommend mold testing and analysis to identify the specific type and extent of mold present. This can involve collecting air samples, surface samples, or even performing a visual inspection of the affected area.
Treatment Options
The treatment for Penicillium mold exposure will depend on the severity of symptoms and the specific health conditions of the individual. Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms, such as antihistamines or bronchodilators for respiratory symptoms, as well as nasal sprays or sinus rinses for sinus symptoms. In some cases, if a fungal infection is present, antifungal medications may be prescribed.
Prevention and Control Measures
Preventing further exposure to Penicillium mold is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may involve taking measures to control moisture and humidity in indoor spaces, such as using dehumidifiers or improving ventilation. Regular cleaning and maintenance, including mold removal from affected surfaces, can also help prevent the growth and spread of Penicillium mold.

When to Seek Medical Help
If you are experiencing symptoms that you suspect may be due to Penicillium mold exposure, it is important to seek medical help. This is especially true if you have pre-existing respiratory conditions or a weakened immune system. Your healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Preventing Penicillium Mold Exposure
Preventing exposure to Penicillium mold is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Here are some prevention strategies to consider:
Maintaining Proper Indoor Air Quality
Good indoor air quality is crucial for preventing the growth and spread of Penicillium mold. This can be achieved by ensuring adequate ventilation in all areas of the home and regularly changing air filters. Air purifiers can also be beneficial in reducing the presence of mold spores in the air.
Controlling Moisture and Humidity
Moisture control is a key factor in preventing Penicillium mold growth. It is important to promptly address any water leaks or sources of excess moisture in the home. Using dehumidifiers in areas prone to high humidity, such as basements or bathrooms, can help maintain optimal humidity levels and discourage mold growth.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent the accumulation of mold spores and the growth of Penicillium mold. Pay special attention to areas where moisture can accumulate, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Clean and dry surfaces regularly and promptly address any signs of water damage or mold growth.
Using Mold-resistant Materials and Products
When renovating or building, consider using mold-resistant materials and products. These include mold-resistant drywall, paints, and caulking. These materials can help minimize the risk of Penicillium mold growth and make it easier to clean and maintain the affected areas.
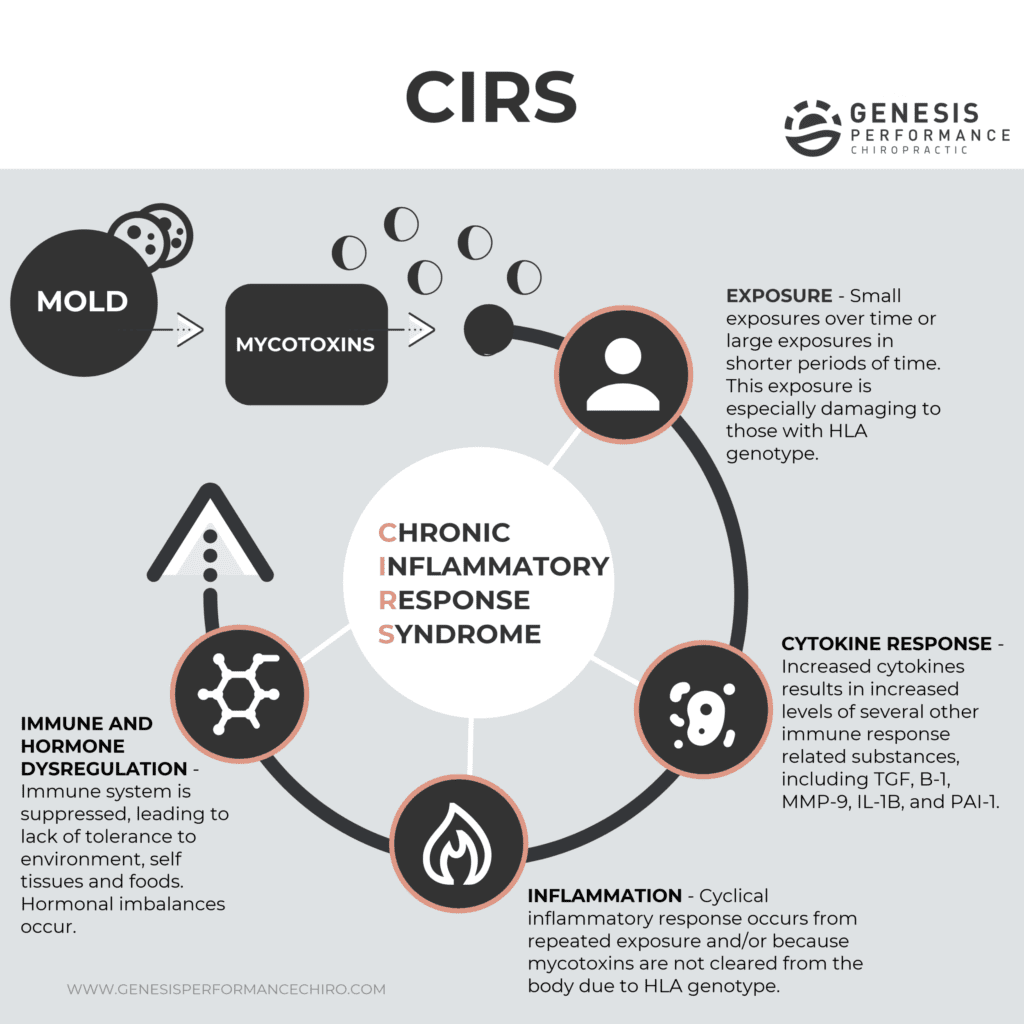
Conclusion
Understanding the potential risks associated with Penicillium mold exposure is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. By being aware of the signs and symptoms of exposure, as well as the complications and long-term effects, you can take the necessary steps to prevent exposure and seek medical help when needed. Remember to prioritize moisture control, regular cleaning and maintenance, and proper ventilation to reduce the risk of Penicillium mold growth in your home or workplace.