If you’ve ever found yourself wondering about the long-term effects of mold exposure on your health, this article is for you. From respiratory issues to chronic fatigue, mold can have a range of detrimental impacts on your well-being. In this informative piece, we will explore the symptoms of mold exposure and the management techniques that can help mitigate its effects on your overall health. So, if you want to learn more about the potential risks of mold and how to protect yourself, keep reading.
Symptoms of Mold Exposure
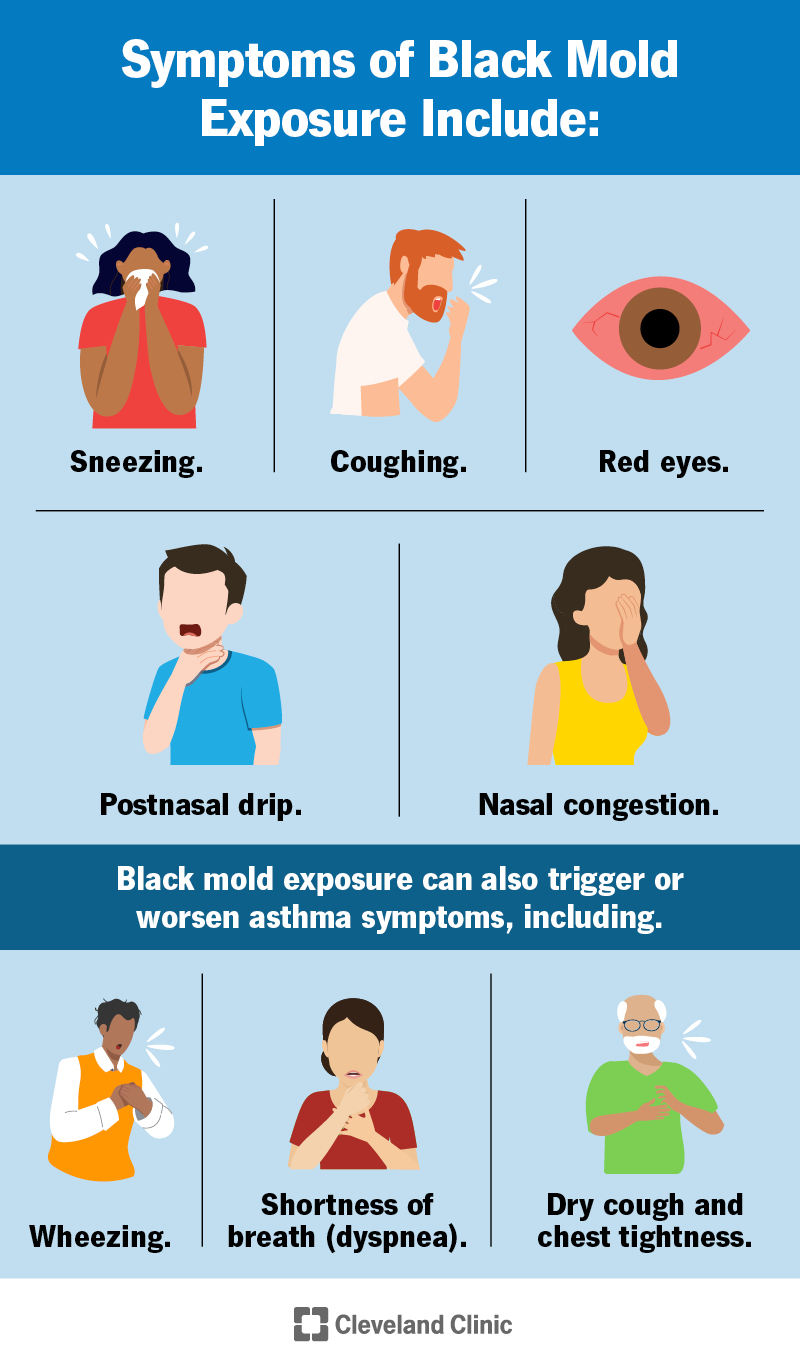
Mold exposure can have a range of physical, respiratory, and skin symptoms. It’s important to be aware of these symptoms so that you can take action to protect your health.
Physical Symptoms
Exposure to mold can often cause physical symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches. You may also experience joint pain and general discomfort. These symptoms can vary from mild to severe, depending on the level of exposure and individual sensitivity. If you notice these physical symptoms occurring regularly, it may be a sign that mold is present in your environment.
Respiratory Symptoms
One of the most common effects of mold exposure is respiratory symptoms. These can include a persistent cough, wheezing or shortness of breath, and a stuffed or runny nose. You might also experience sinus congestion and sore throat. If you find that these respiratory symptoms worsen when you are in a certain environment or specific area of your home, it’s important to investigate for potential mold sources.
Skin Symptoms
In some cases, mold exposure can lead to skin symptoms. These can include rashes, itching, and redness on the skin. You may also experience dry, flaky skin or notice small bumps or hives. If you have a history of skin allergies or sensitivities, you may be more prone to developing these symptoms when exposed to mold. It is essential to pay attention to any changes in your skin and seek medical advice if necessary.
Long-Term Health Effects
While short-term mold exposure symptoms can be uncomfortable, long-term exposure can have more serious health effects. It’s important to understand the potential risks and seek appropriate management strategies.
Respiratory Disorders
Long-term mold exposure can contribute to the development or exacerbation of respiratory disorders such as chronic bronchitis or pneumonia. Prolonged exposure to mold spores can irritate and inflame the airways, making it difficult to breathe. This can lead to persistent coughing, recurring respiratory infections, and even more severe respiratory conditions.
Allergies and Asthma
For individuals with allergies or asthma, mold exposure can trigger or worsen these conditions. Mold spores can act as allergens, triggering allergic reactions such as sneezing, itching, and watery eyes. Additionally, the presence of mold in the environment can cause asthma symptoms to become more frequent and severe, leading to coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. It’s crucial for individuals with allergies or asthma to be vigilant about minimizing mold exposure to manage their symptoms effectively.
Neurological Effects
There is growing evidence to suggest that long-term mold exposure may have neurological effects. Some studies have linked mold exposure to cognitive impairments, memory problems, and general brain fog. While more research is needed, it’s important to be aware of these potential effects and take steps to reduce exposure to mold in your living and working environments.

Management of Mold Exposure
If you suspect mold exposure or have experienced symptoms related to mold exposure, there are several steps you can take to manage the situation effectively.
Identifying and Eliminating Mold Sources
The first step in managing mold exposure is identifying and eliminating the sources of mold. Mold thrives in areas with high humidity or dampness, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Check these areas for visible signs of mold, such as discoloration or a musty odor. It’s also important to address any water leaks or moisture issues promptly to prevent mold growth. If you find mold, it’s crucial to clean it properly or consult a professional to ensure safe and effective removal.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is another essential aspect of managing mold exposure. Mold spores can become airborne and be inhaled, contributing to health issues. To minimize the risk, ensure proper ventilation in your home or workplace by opening windows or using fans. Use air purifiers or filters to remove airborne particles, including mold spores. Regularly clean and vacuum your living and working spaces to reduce the accumulation of dust and mold spores.
Seeking Medical Treatment
If you are experiencing symptoms related to mold exposure, it’s important to seek medical treatment. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, provide appropriate treatment, and offer guidance on managing your exposure. They may recommend medications to alleviate respiratory symptoms or refer you to an allergist or pulmonologist for further evaluation and management. Additionally, they can help identify any potential underlying health conditions that may be aggravated by mold exposure.
In conclusion, being aware of the symptoms of mold exposure and understanding the long-term health effects is crucial for protecting your well-being. By taking proactive steps to manage mold exposure, such as identifying and eliminating mold sources, improving indoor air quality, and seeking medical treatment when necessary, you can minimize the negative health impacts and create a healthier living environment for yourself. Remember, your health is important, and addressing any potential mold-related issues promptly can help ensure a healthier and happier life.