If you’ve ever wondered whether mold exposure could have long-lasting effects on your health, you’re not alone. Many people are concerned about the potential consequences of being exposed to mold in their homes or workplaces. This article explores the question of whether mold exposure is permanent and aims to shed light on this important topic.

Understanding Mold Exposure
Mold is a type of fungus that can grow both indoors and outdoors. It commonly thrives in damp and humid environments, such as basements, bathrooms, and areas with water damage. Mold reproduces through tiny spores that can be easily inhaled, leading to possible health effects.
What is Mold?
Mold is a common type of fungus that plays an important role in breaking down dead organic matter in the environment. It comes in various colors, such as black, green, or white, and can have a musty odor. Mold spores are microscopic and can be found everywhere, both indoors and outdoors. Mold can grow on almost any surface, including wood, carpet, drywall, and fabric.
How Does Mold Exposure Occur?
Exposure to mold can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Mold spores can become airborne and easily inhaled when disturbed, such as during cleaning or renovation activities. Ingesting mold can happen if contaminated food or beverages are consumed. Skin contact with mold can cause irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
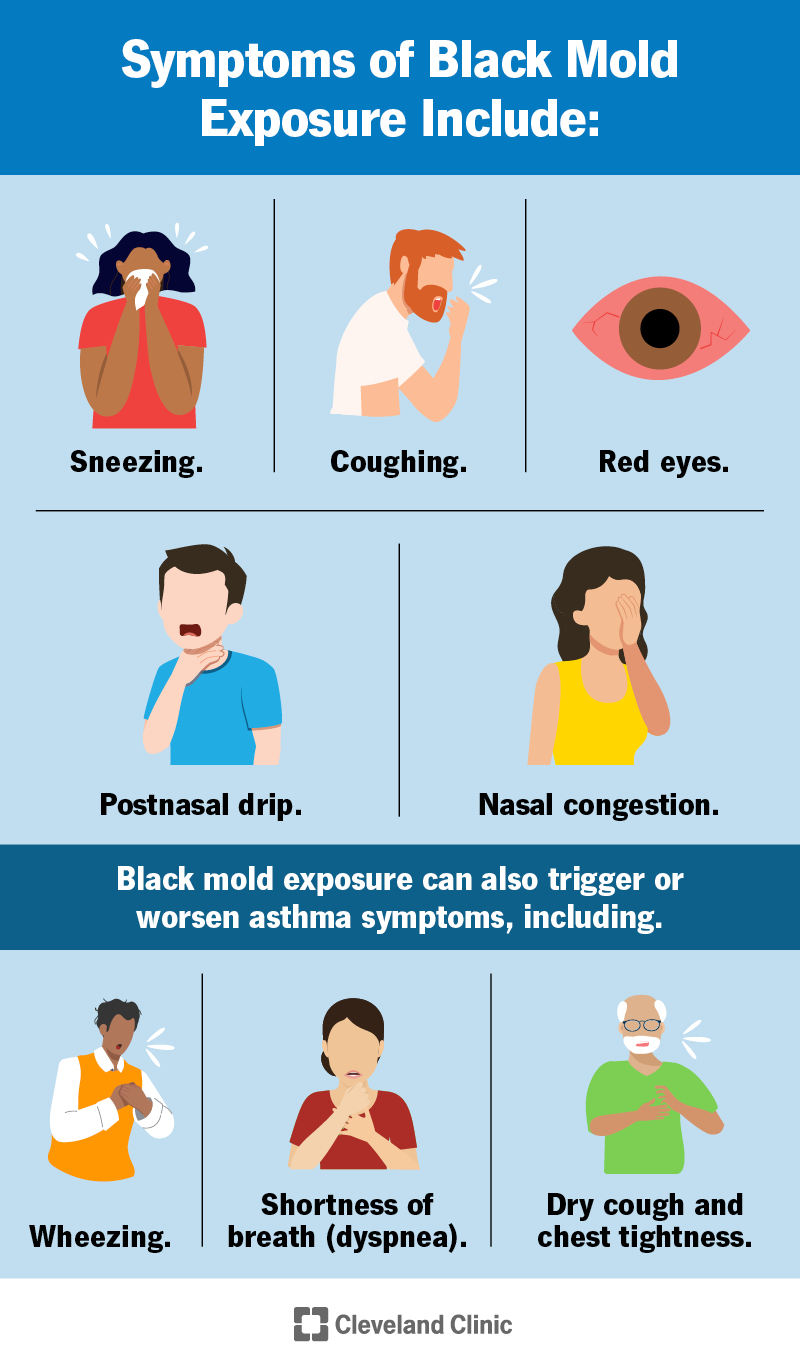
Common Health Effects of Mold Exposure
Mold exposure can lead to a range of health effects, both short-term and long-term. The severity of these effects can vary depending on the duration and intensity of exposure, as well as individual sensitivity and underlying health conditions.

Short-Term Effects of Mold Exposure
Respiratory Issues
One of the most common short-term health effects of mold exposure is respiratory issues. Inhaling mold spores can irritate the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. For individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), mold exposure can exacerbate their symptoms.
Allergic Reactions
Many people are allergic to mold, and exposure can trigger allergic reactions. Symptoms may include sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, and skin rash. These reactions can range from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s sensitivity to mold.
Irritation of the Skin, Eyes, and Throat
Direct contact with mold or mold-infested materials can cause irritation of the skin, eyes, and throat. This can result in redness, itchiness, swelling, and soreness. In some cases, exposure to certain types of mold can also lead to more severe skin conditions or respiratory irritation.
Long-Term Effects of Mold Exposure
Chronic Respiratory Conditions
Prolonged exposure to mold can potentially contribute to the development of chronic respiratory conditions. This includes conditions such as chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic lung diseases are particularly vulnerable to these long-term effects.
Asthma
Mold exposure has been linked to the development of asthma in both children and adults. Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, resulting in recurrent episodes of wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
Fungal Infections
In some cases, mold exposure can lead to fungal infections. When mold spores are inhaled and reach the lungs, they can potentially cause infections such as aspergillosis or fungal pneumonia. These infections can be severe, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
Toxic Mold Syndrome
There is growing concern about the potential health risks associated with exposure to certain types of mold known as “toxic molds.” Toxic molds produce mycotoxins, which are toxic substances that can have adverse effects on human health, even in low concentrations. Symptoms of toxic mold syndrome can include fatigue, headache, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and respiratory issues.

Factors Influencing the Persistence of Mold Exposure
Duration and Intensity of Exposure
The longer and more intense the exposure to mold, the greater the potential for health effects. Continuous exposure to high levels of mold can have more severe and lasting impacts on an individual’s health.
Individual Sensitivity
Each person’s tolerance to mold varies. Some individuals may be more sensitive and experience symptoms with even minimal exposure, while others may not show any immediate effects. Factors such as age, overall health, and genetic predisposition can influence an individual’s sensitivity to mold.
Underlying Health Conditions
People with weakened immune systems, chronic respiratory conditions, or allergies may be more susceptible to the health effects of mold exposure. These underlying health conditions can make individuals more vulnerable to respiratory infections and exacerbate existing symptoms.
Treatment and Remediation
Prompt and effective treatment and remediation play a significant role in mitigating the persistence and severity of mold exposure. Treating any associated health conditions and addressing the underlying causes of mold growth are crucial steps in reducing the impact of mold exposure.
Potential for Mold Exposure Recovery
Reducing Exposure
Reducing exposure to mold is essential for recovery. This involves eliminating or controlling the source of mold, improving ventilation and air circulation, and keeping indoor humidity levels below 50 percent. Regular cleaning and maintenance, especially in areas prone to moisture, can also help prevent mold growth.
Professional Mold Remediation
In cases of severe mold infestation, professional mold remediation may be necessary. Trained professionals can identify and safely remove mold, ensuring thorough cleaning to prevent further contamination. Additionally, they can assess and address any underlying issues that may be contributing to mold growth, such as water leaks or inadequate ventilation.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is crucial for recovering from mold exposure. This can be achieved by using air purifiers with HEPA filters, practicing good ventilation, and regularly changing air filters in HVAC systems. Additionally, keeping a clean and clutter-free environment can minimize the accumulation of dust and moisture, which can promote mold growth.

Prevention and Protection against Mold Exposure
Controlling Moisture Levels
Preventing excessive moisture is crucial in preventing mold growth. This includes fixing any water leaks, ensuring proper drainage, and using dehumidifiers in areas prone to high humidity. Regularly inspecting and maintaining areas susceptible to water damage, such as roofs, plumbing, and foundations, is also essential.
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation helps to maintain balanced moisture levels and prevent stagnant air. Adequate ventilation systems, such as exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms, can help remove excess moisture and humidity. Opening windows and using fans in high moisture areas can also improve air circulation and reduce the risk of mold growth.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are vital in preventing mold growth and ensuring a healthy indoor environment. This includes wiping down surfaces with mold-resistant cleaners, promptly drying any areas affected by water damage, and regularly cleaning ventilation systems and air filters. Removing clutter and excess moisture-prone materials also helps create an environment less conducive to mold growth.
Avoiding High-Risk Environments
Avoiding or minimizing exposure to high-risk environments is another preventive measure against mold exposure. This includes avoiding areas with visible mold growth or known water damage, as well as staying away from buildings or environments where mold-related issues have been reported.
Seeking Medical Assistance
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of mold exposure is crucial in seeking timely medical assistance. Common symptoms include respiratory issues, allergic reactions, skin irritation, persistent coughing, fatigue, and headaches. If you experience these symptoms and suspect mold exposure, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Importance of Professional Diagnosis
Professional diagnosis is essential in determining the cause and extent of mold exposure. Healthcare professionals can conduct tests to identify specific allergens or irritants causing symptoms and evaluate the overall impact on the individual’s health. This enables appropriate treatment and management strategies to be implemented.
Treatment Options
The treatment of mold exposure primarily involves addressing any associated health conditions and symptoms. This may include the use of medications such as antihistamines, nasal sprays, or bronchodilators to alleviate respiratory symptoms. In severe cases, the individual may require hospitalization or specialized treatments for fungal infections.
Follow-Up and Monitoring
Follow-up and ongoing monitoring are essential to assess the individual’s response to treatment and identify any long-term health effects. Regular medical check-ups and evaluations help ensure proper management of respiratory conditions, assess lung function, and address any potential complications or residuals of mold exposure.
Legal Implications of Mold Exposure
Landlord and Tenant Responsibilities
Mold exposure in rented properties often raises legal questions regarding the responsibilities of landlords and tenants. Landlords have an obligation to provide and maintain safe and habitable living conditions, which includes addressing and remedying mold issues promptly. Tenants, on the other hand, are responsible for reporting any concerns about mold growth and practicing proper maintenance to prevent further mold-related problems.
Employer and Employee Rights
In the workplace, employers have a duty to provide a safe and healthy environment free from potential hazards, including mold. Employees have the right to notify employers about any observed mold growth or concerns and request remediation. If employers fail to address mold-related issues appropriately, employees may have legal recourse to ensure a safe working environment.
Lawsuits and Liability
Mold exposure can sometimes lead to legal actions and lawsuits, particularly when negligence or inadequate remediation is involved. Lawsuits may seek compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, property damage, and pain and suffering. It is important to consult legal professionals experienced in mold-related matters to understand legal rights and pursue appropriate legal actions.
Mold Exposure and Property Damage
Structural Integrity Effects
Mold growth can have detrimental effects on the structural integrity of buildings and properties. Over time, mold can cause wood rot, deterioration of drywall, and damage to other building materials. This can weaken the structural components and compromise the safety and longevity of the property.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage for mold-related damages and remediation can vary depending on the specific policy terms and conditions. Some insurance policies may provide coverage for mold remediation costs, while others may have exclusions or limitations. It is important to review and understand your insurance coverage and consider obtaining additional coverage if necessary.
Remediation Costs
Remediation costs can vary widely depending on the extent of the mold infestation and the complexity of the remediation process. Factors such as the size of the affected area, the severity of the mold growth, and the need for specialized equipment or professional services can contribute to overall costs. It is advisable to consult with reputable mold remediation professionals to assess and estimate the required remediation costs accurately.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing mold exposure is crucial for maintaining a healthy living or working environment. Mold exposure can have both short-term and long-term health effects, making prevention, prompt remediation, and proper medical attention essential. By implementing preventive measures, seeking professional assistance when needed, and advocating for improved regulations and standards, individuals and communities can strive for better protection against the potential health and property damage risks associated with mold exposure.