In this article, you will learn about the symptoms of mold exposure and how it can affect your health. Mold is a common problem in many homes and can cause allergies, respiratory issues, and other health problems. By recognizing the symptoms of mold exposure, you can take steps to protect yourself and your family. From coughing and sneezing to fatigue and skin irritation, we will explore the various ways that mold can impact your well-being. Stay tuned to better understand the effects of mold and how to maintain a healthy indoor environment.
What is Mold and How Does It Enter the Body?
Mold is a type of fungus that can be found both indoors and outdoors. It thrives in damp and humid conditions, where it reproduces by releasing spores into the air. When these spores are inhaled or come into contact with the body, they can enter the respiratory system and cause a range of health problems.
Understanding the Basics of Mold
Mold is commonly found in areas with excessive moisture, such as bathrooms, basements, and kitchens. It can grow on various surfaces, including walls, carpets, furniture, and even clothing. Mold can appear in different colors, including black, green, and white.
When mold grows, it releases spores into the air. These spores are incredibly small and lightweight, allowing them to be easily inhaled. Once inside the body, mold spores can trigger a range of physical symptoms and even affect our psychological well-being.
Common Ways Mold Enters the Body
There are several ways in which mold can enter the body:
-
Inhalation: Breathing in mold spores is the most common route of exposure. When mold-infested materials are disturbed, such as during cleaning or renovation, spores can become airborne and easily inhaled.
-
Skin Contact: Direct contact with mold-infested surfaces or objects can lead to skin problems, such as rashes or hives. This is particularly true for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies.
-
Ingestion: Although less common, mold can enter the body through ingestion. This can occur when food or beverages contaminated with mold are consumed. Eating moldy food can cause a range of digestive problems.
Physical Symptoms of Mold Exposure
Exposure to mold can cause a variety of physical symptoms, which may vary depending on the individual and the duration of exposure. It’s important to recognize these symptoms in order to identify and address mold-related health issues.
Respiratory Issues
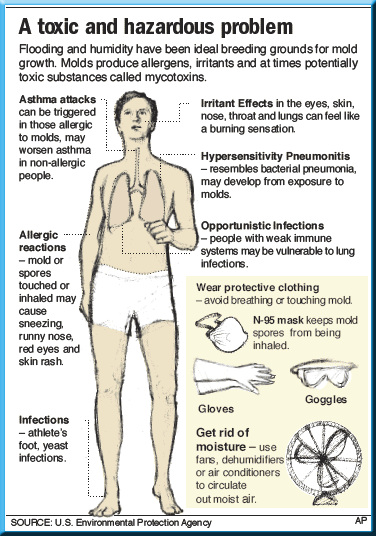
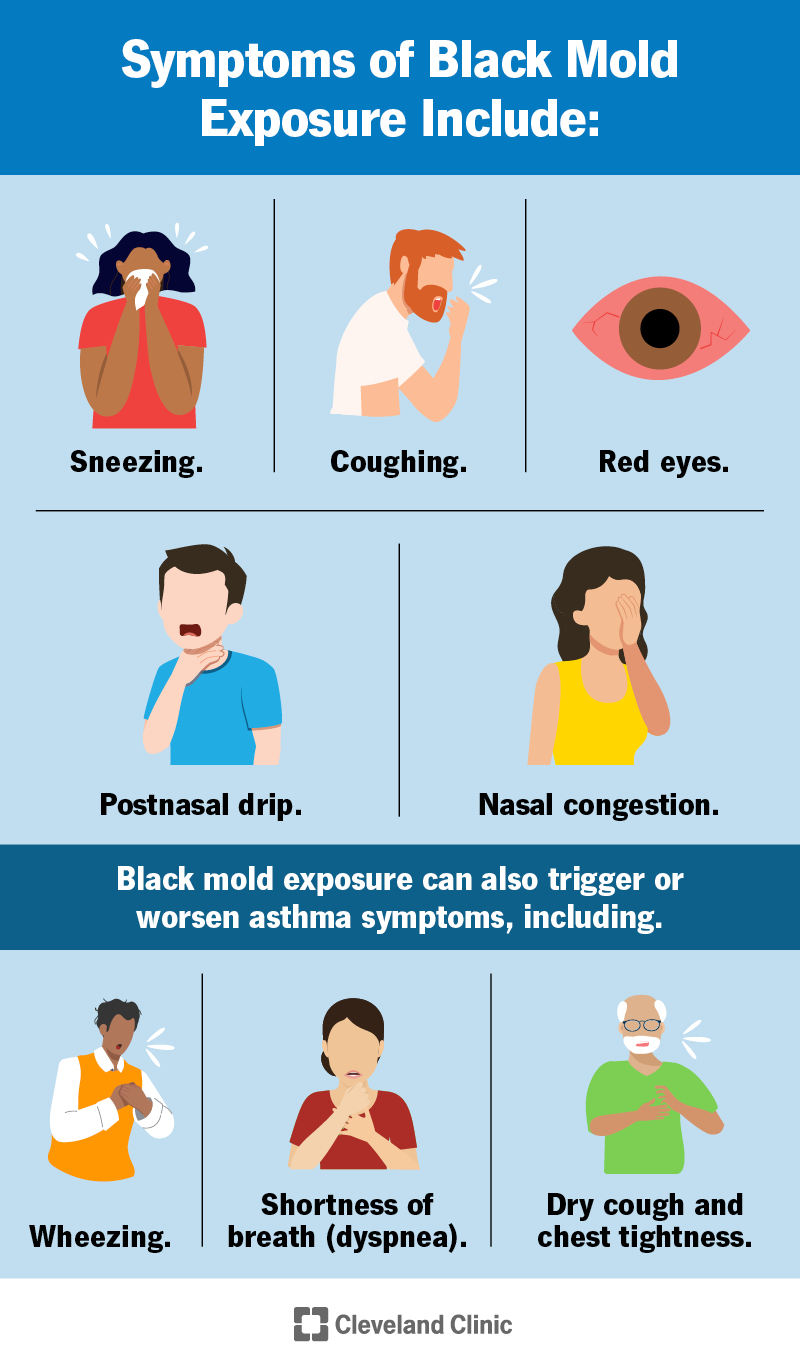
One of the most common physical symptoms of mold exposure is respiratory problems. Inhaling mold spores can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and even asthma attacks in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Skin Problems
Direct contact with mold-infested surfaces can result in skin problems. This can include rashes, hives, itching, and redness. Individuals with existing skin conditions, such as eczema, may be more prone to experiencing these symptoms.
Allergic Reactions
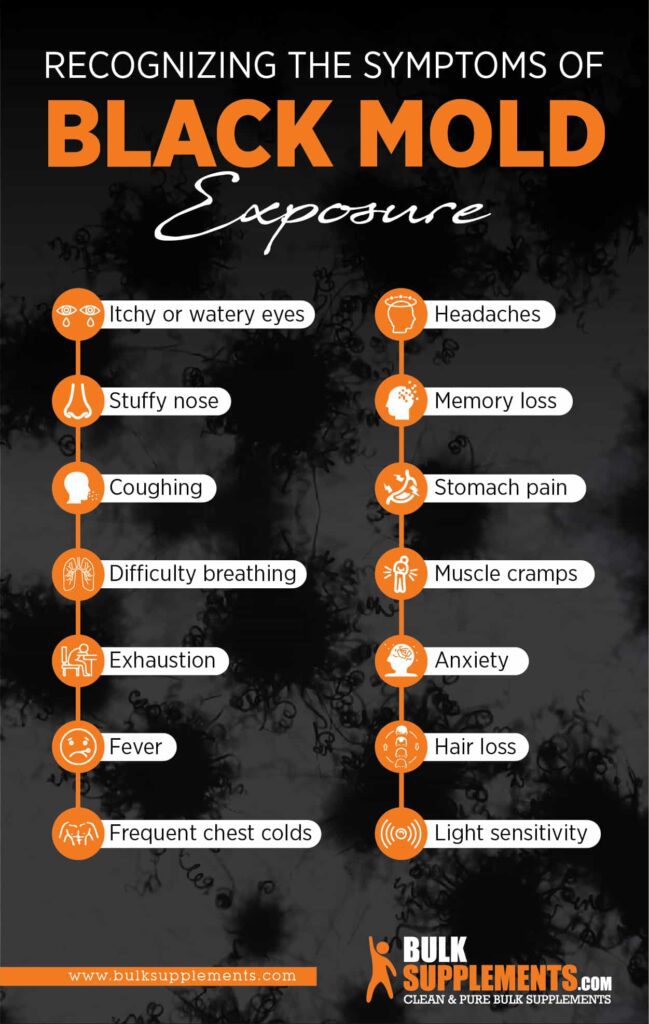
For individuals who are allergic to mold, exposure can trigger allergic reactions. Symptoms may include sneezing, nasal congestion, itchy and watery eyes, and a runny or stuffy nose. These symptoms are similar to those experienced with seasonal allergies.
Headaches and Fatigue
Extended exposure to mold can also lead to chronic headaches and fatigue. These symptoms can be debilitating and impact daily functioning. Headaches may range from mild to severe, while fatigue can leave individuals feeling constantly tired and lacking energy.
Eye and Vision Issues
Mold exposure can also affect the eyes and vision. Itchy, red, and watery eyes are common symptoms, along with blurred vision. These symptoms may subside once the individual is no longer exposed to mold.
Digestive Problems
Ingestion of mold-contaminated food or beverages can result in various digestive issues. This can include stomach pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. Mold produces mycotoxins, which can cause irritation and inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
Psychological and Cognitive Symptoms
In addition to physical symptoms, mold exposure can also have psychological and cognitive effects. These symptoms can be particularly challenging, as they often go unrecognized or are attributed to other causes.
Anxiety and Depression
Exposure to mold has been linked to increased levels of anxiety and depression. This may be due to the impact mold has on overall health and well-being, as well as the chronic nature of the symptoms it causes.
Memory and Concentration Issues
Individuals exposed to mold may experience difficulties with memory and concentration. This can manifest as forgetfulness, difficulty focusing, and impaired cognitive function. These symptoms can have a significant impact on daily life and productivity.
Mood Swings and Irritability
Mold exposure can affect mood regulation, leading to mood swings and increased irritability. Individuals may find themselves feeling more easily frustrated, angry, or overwhelmed. These emotional changes can strain relationships and overall mental well-being.
Confusion and Disorientation
In some cases, mold exposure can cause confusion and disorientation. This can present as difficulty with decision-making, trouble remembering details, or feeling mentally foggy. These symptoms can be particularly distressing and require medical attention.
Impact of Mold Exposure on the Immune System
Exposure to mold can have a profound effect on the immune system. Mold spores and mycotoxins can trigger immune responses, leading to a range of health complications.
Weakening of the Immune Response
Prolonged exposure to mold can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. The immune system becomes overworked in an attempt to combat the constant presence of mold in the body.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
A weakened immune system can result in an increased risk of infections. Individuals exposed to mold may experience frequent respiratory infections, sinusitis, and other bacterial or viral infections.
Autoimmune Reactions
Exposure to mold has been linked to the development of autoimmune disorders. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and a range of symptoms that vary depending on the specific autoimmune condition.
Chronic Inflammation
Mold exposure can also lead to chronic inflammation throughout the body. Inflammation is a normal immune response, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to the development of various health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurological disorders.

Long-term Health Effects
If left untreated, mold exposure can have long-term health effects. These effects can manifest in various systems of the body and may have a significant impact on overall well-being.
Respiratory Disorders
Prolonged exposure to mold can contribute to the development of respiratory disorders, such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These conditions can be chronic and require ongoing medical management.
Neurological Disorders
Mold exposure has been linked to the development of neurological disorders, including memory loss, cognitive decline, and neurological symptoms similar to those seen in multiple sclerosis (MS). The exact mechanisms by which mold affects the brain are still being studied.
Cardiovascular Complications
Chronic inflammation caused by mold exposure can increase the risk of cardiovascular complications. This includes conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It is important to address mold-related health issues in order to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Reproductive and Hormonal Issues
Exposure to mold can also impact reproductive and hormonal health. Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles, fertility problems, and an increased risk of complications during pregnancy. In men, mold exposure has been associated with decreased sperm count and fertility issues.
Vulnerable Population Groups
Certain population groups may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of mold exposure. It is important to pay special attention to these groups and take appropriate measures to prevent and address mold-related health issues.
Children
Children have developing immune systems and respiratory systems, making them more vulnerable to the effects of mold exposure. They may experience more severe symptoms and are at an increased risk of developing respiratory disorders.
Elderly Individuals
As we age, our immune system weakens, making elderly individuals more susceptible to the adverse effects of mold exposure. They may experience more severe symptoms, have a harder time recovering, and be at an increased risk of developing complications.
Pregnant Women
Exposure to mold during pregnancy can pose risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. It is important for pregnant women to be aware of potential mold exposure and take steps to minimize it. Mold-related respiratory issues can also impact the health of the developing baby.
Immunocompromised Individuals
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at a higher risk of complications from mold exposure. The immune system may struggle to combat the presence of mold, leading to more severe symptoms and an increased risk of infections.

Diagnosing Mold-related Illnesses
Diagnosing mold-related illnesses can be challenging, as symptoms can vary widely and overlap with other conditions. However, there are steps that healthcare professionals can take to identify mold-related health issues.
Medical History and Symptom Assessment
The first step in diagnosing a mold-related illness is a thorough medical history and symptom assessment. This includes discussing any exposure to mold, the duration and severity of symptoms, and any other relevant information.
Blood Tests and Immunological Markers
Blood tests can be helpful in identifying immune system responses to mold exposure. Elevated levels of certain antibodies may indicate an allergic reaction or ongoing immune response. Immunological markers can help determine the presence or severity of mold-related health issues.
Mold Spore and Mycotoxin Testing
In some cases, mold spore and mycotoxin testing may be conducted to confirm mold exposure. This can involve air sampling or surface sampling to identify the presence and type of mold in a particular environment. Testing can provide valuable information for effective treatment and remediation strategies.
Treating Mold-related Health Problems
Treating mold-related health problems involves a multidimensional approach that includes identifying and addressing the source of mold, managing symptoms, and supporting the immune system.
Removing the Source of Mold
The first and most important step in treating mold-related health issues is to remove the source of mold. This may involve professional mold remediation services to properly clean and eliminate mold growth from affected areas. It’s important to fix any underlying moisture problems to prevent future mold growth.
Medication and Symptom Management
Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with mold exposure. For example, antihistamines can help relieve allergic reactions, while bronchodilators can help manage respiratory symptoms. Corticosteroids may be prescribed for more severe symptoms.
Supporting the Immune System
Supporting the immune system is crucial in addressing mold-related health problems. This may involve a combination of lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Supplements or medications that boost immune function may also be recommended.
Environmental Remediation
In addition to removing the source of mold, it may be necessary to address any lingering mold spores or mycotoxins in the environment. This can include thorough cleaning, use of air purifiers, and improving ventilation to prevent future mold growth. Consulting with professionals in environmental remediation can ensure proper measures are taken.
Preventing Mold Exposure
Preventing mold exposure is key to protecting your health and well-being. By implementing proactive measures, you can reduce the risk of mold-related health issues.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections of your home or workplace can help identify and address potential sources of mold. This includes checking for water leaks, condensation, and any signs of water damage. Promptly addressing these issues can prevent mold growth.
Proper Ventilation and Indoor Air Quality
Proper ventilation is important in reducing moisture levels and preventing the buildup of mold. Ensure that bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas prone to moisture have proper ventilation systems in place. Maintaining good indoor air quality also involves keeping humidity levels below 50% and using air purifiers if necessary.
Effective Moisture Control
Moisture control is essential in preventing mold growth. This can include promptly repairing any leaks, drying wet areas within 24-48 hours, and using dehumidifiers in humid environments. Regularly checking for and addressing any excess moisture can prevent mold from taking hold.
Prompt Water Damage Restoration
In the event of water damage, such as flooding or leaks, it is crucial to promptly address the issue. Water damage creates an ideal environment for mold growth. Quick and thorough restoration is necessary to prevent mold from spreading and causing health problems.
Conclusion
Being aware of the body symptoms of mold exposure is crucial in recognizing the effects mold can have on your health. Mold can enter the body through inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion, leading to a variety of physical, psychological, and cognitive symptoms. Long-term exposure to mold can have serious repercussions for the immune system and overall health. It is important to identify and treat mold-related illnesses promptly to avoid further complications. By taking preventive measures, such as regular inspections, proper ventilation, and moisture control, you can minimize the risk of mold exposure and protect your well-being. Remember, recognizing the impact of mold exposure is the first step towards addressing and preventing its negative effects on your health.