Have you ever wondered how long it takes to treat mold in a house? Mold can be a pesky problem that not only affects the appearance of your home but also poses health risks to you and your family. In this article, we will explore the different factors that can influence the time it takes to treat mold in a house and provide you with some insights on what to expect during the process. So, if you’re dealing with mold-related issues and want to know how long it might take to get your home mold-free, keep reading!
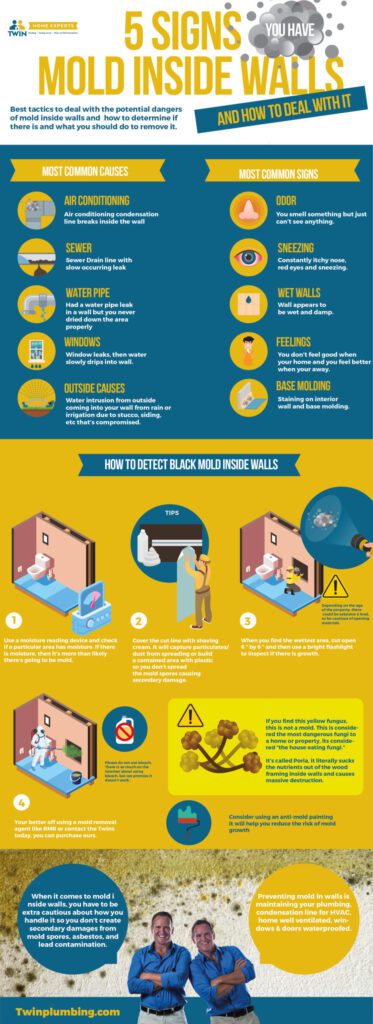
Assessing the Severity of Mold Infestation
Determining the Types of Mold Present
When dealing with a mold infestation, it is crucial to determine the types of mold present in your house. Different types of mold can pose different health risks and require specific remediation methods. A professional mold inspector or a certified laboratory can analyze samples collected from your property to identify the specific types of mold present.
Inspecting the Extent of Mold Growth
In order to effectively address the mold problem in your house, you need to inspect the extent of mold growth. This involves a thorough assessment of all areas affected by mold, including hidden areas such as behind walls or under carpets. A comprehensive inspection will help determine the scope of the remediation process and the level of damage caused by the mold.
Identifying the Underlying Cause of Mold
To prevent future mold growth, it is important to identify and address the underlying cause of the mold infestation. Mold usually thrives in damp and humid environments, so it is crucial to locate the source of moisture that is promoting mold growth. Common sources of moisture intrusion include leaks in plumbing systems, roof leaks, poor ventilation, and high humidity levels. By identifying and fixing these underlying issues, you can prevent mold from recurring in the future.
Assessing the Structural Damage
Mold infestations can cause structural damage to your property, especially if left untreated for a long time. During the assessment process, it is important to thoroughly inspect the affected areas for any signs of structural damage. This can include weakened walls, deteriorated insulation, or compromised flooring. Assessing the structural damage will help determine if any repairs or replacements are necessary as part of the remediation process.
Sampling for Airborne Mold Spores
In order to assess the air quality and determine the potential health risks associated with the mold infestation, it is important to conduct sampling for airborne mold spores. This involves collecting air samples from different areas of your house and analyzing them in a laboratory. By measuring the concentration of mold spores in the air, you can better understand the extent of the contamination and the potential health risks for you and your family.
Developing a Mold Remediation Plan
Creating a Containment Strategy
Before beginning the mold remediation process, it is important to create a containment strategy to prevent the spread of mold spores to unaffected areas of your house. This involves isolating the mold-infested areas by sealing them off with plastic sheets and using air filtration devices to create negative air pressure. Creating an effective containment strategy will help ensure that the mold spores are not dispersed to other parts of your house during the remediation process.
Establishing Safety Measures
The safety of both the occupants and the remediation professionals is of utmost importance during the mold removal process. Proper safety measures should be established to minimize the risk of exposure to mold spores and hazardous materials. This can include wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and goggles, as well as implementing proper ventilation to ensure good air circulation.
Setting Up Air Filtration Devices
To further enhance air quality and control the spread of mold spores, it is important to set up air filtration devices throughout the mold-infested areas. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can effectively trap airborne mold spores and prevent their circulation to other parts of your house. By continuously filtering the air, these devices can significantly improve the overall air quality during the remediation process.
Outlining the Scope of Work
A comprehensive mold remediation plan should outline the scope of work required to successfully remove the mold and restore the affected areas. This includes detailing the specific areas to be remediated, the methodology to be used, and the timeline for each step of the process. By clearly outlining the scope of work, you can ensure that all necessary tasks are identified and completed effectively.
Determining the Necessary Equipment and Materials
To successfully remediate a mold infestation, it is essential to determine the necessary equipment and materials needed for the job. This can include various tools for mold removal, such as scrub brushes, sprayers, and containment supplies. Additionally, specific chemicals and biocides may be required to effectively kill and remove the mold. By properly determining the necessary equipment and materials, you can ensure that the mold removal process is carried out efficiently and effectively.

Removal of Mold-Infested Materials
Removing Mold from Non-Porous Surfaces
Non-porous surfaces such as glass, metal, or plastic can usually be effectively cleaned and disinfected to remove mold growth. Using appropriate cleaning agents and techniques, mold can be physically removed from these surfaces. It is important to ensure that all visible mold is completely removed and that the surfaces are thoroughly dried to prevent any residual spores from regrowth.
Discarding Porous Materials with Mold Growth
Porous materials, such as fabrics, carpeting, drywall, and insulation, are more susceptible to mold growth and are often difficult to clean and salvage. In many cases, it is recommended to discard these materials as they can easily retain moisture and harbor hidden mold. Removing and properly disposing of mold-infested porous materials is essential to prevent further contamination and ensure effective mold remediation.
Treating Semi-Porous Materials
Semi-porous materials, such as wood or concrete, can pose a challenge when it comes to mold removal. These materials may require specialized treatment methods to effectively eliminate mold. Techniques such as sanding, wire brushing, or using specific biocides may be necessary to remove mold from semi-porous surfaces. It is important to follow industry best practices and manufacturer guidelines when treating these materials to ensure proper and safe removal of mold.
Cleaning and Disinfecting Contents
During the mold remediation process, it is also important to clean and disinfect any affected contents such as furniture, appliances, or personal belongings. Proper cleaning and disinfection techniques should be employed to remove mold spores from these items. It is essential to thoroughly dry and ventilate the contents to prevent any residual moisture and discourage further mold growth.
Addressing Mold Contamination in HVAC Systems
Inspecting and Cleaning Air Ducts
Mold contamination in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems can easily spread mold spores throughout your house. It is crucial to inspect and clean the air ducts and vents to remove any mold and prevent its dissemination. Professional HVAC technicians can use specialized equipment and cleaning methods to effectively remove mold from the ductwork and improve the air quality of your house.
Cleaning and Replacing Filters
Regularly cleaning or replacing the filters in your HVAC system is important to prevent the accumulation and spread of mold spores. Mold can easily grow on dirty or clogged filters, and the air passing through them can distribute mold spores to different areas of your house. By keeping your filters clean and replacing them according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, you can minimize the risk of mold contamination in your HVAC system.
Cleaning HVAC Components
In addition to the air ducts and filters, other components of your HVAC system, such as coils and condensation pans, can also become contaminated with mold. These components should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected to remove any mold growth. Regular maintenance of your HVAC system, including the cleaning of these components, can help prevent mold growth and improve the overall air quality in your house.
Eliminating Mold Colonies in HVAC Systems
If mold colonies have developed within your HVAC system, more extensive measures may be necessary to eliminate the mold. In such cases, professional mold remediation companies may use specialized techniques, such as fogging or applying antimicrobial treatments, to effectively address the mold growth within the system. Properly eliminating mold colonies in your HVAC system is crucial to prevent the recirculation of mold spores and improve the overall air quality of your house.

Applying Mold Removal Techniques
Surface Cleaning with Biocides
Surface cleaning with biocides is a common method used for mold removal. Biocides are substances that can effectively kill mold spores on contact. When applying biocides, it is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and use appropriate protective equipment. Surface cleaning with biocides can effectively remove and kill mold on non-porous materials and surfaces.
Dry Ice Blasting or Media Blasting
Dry ice blasting and media blasting are advanced mold removal techniques that involve using high-pressure streams of dry ice or specialized abrasive media to remove mold from surfaces. These techniques are often used on larger or more complex mold remediation projects. Dry ice blasting or media blasting can effectively remove mold from surfaces without causing damage or leaving residue behind.
Non-Toxic Mold Removal Methods
For those concerned about the use of chemicals and biocides, non-toxic mold removal methods can be employed. These methods focus on using natural or environmentally friendly substances to remove and kill mold. Examples include vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, or tea tree oil. Non-toxic mold removal methods can be effective for smaller or less severe mold infestations.
HEPA Vacuuming of Mold Spores
To further minimize the spread of mold spores during the remediation process, HEPA vacuuming can be utilized. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) vacuums are designed to capture extremely small particles, including mold spores. By vacuuming affected areas with a HEPA vacuum, mold spores can be effectively removed from surfaces and the air, reducing the risk of further contamination.
Encapsulation of Mold-Infested Areas
In some cases, encapsulation may be used as a method to contain and control mold growth. Encapsulation involves applying a specialized coating or barrier to mold-infested surfaces to prevent the release of mold spores. This technique can be particularly useful for areas that are difficult to access or clean, such as crawlspaces or attics. Proper encapsulation can help prevent further mold growth and reduce the risk of exposure to mold spores.
Drying and Dehumidifying the Affected Areas
Using High-Efficiency Dehumidifiers
After removing the mold and addressing the underlying cause of moisture, it is important to thoroughly dry the affected areas. High-efficiency dehumidifiers can help remove excess moisture from the air and accelerate the drying process. By maintaining optimal humidity levels, you can prevent further mold growth and promote the drying of structural materials.
Employing Air Movers and Fans
In conjunction with dehumidifiers, the use of air movers and fans can aid in the drying process by promoting air circulation and evaporation. These devices help to reduce the moisture content in the affected areas, speeding up the drying time and preventing the potential for residual moisture to lead to mold regrowth. Proper placement and operation of air movers and fans are crucial to optimize the drying process.
Monitoring Moisture Levels
Throughout the drying process, it is important to monitor the moisture levels in the affected areas. Moisture meters or hygrometers can be used to accurately measure the moisture content in materials and the air. Regular monitoring allows for adjustments to the drying equipment and techniques, ensuring that the affected areas reach an acceptable level of dryness and are less susceptible to further mold growth.

Preventing Future Mold Growth
Fixing the Source of Moisture Intrusion
Preventing future mold growth requires addressing the source of moisture intrusion. Whether it is a leaky pipe, roof, or inadequate ventilation, identifying and fixing the source is crucial. Repairing any issues that contribute to excess moisture will help create an environment inhospitable to mold growth.
Improving Ventilation and Air Circulation
Improving ventilation and air circulation is key to preventing mold growth, as mold thrives in stagnant, humid air. Properly ventilating areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements can help reduce moisture levels and minimize the risk of mold growth. Additionally, utilizing fans and air purifiers can aid in promoting air circulation and improving overall indoor air quality.
Sealing Cracks and Leaks
Small cracks and leaks in the construction of your house can provide entry points for moisture and mold. Sealing these cracks and fixing any gaps or leaks in the building envelope can help prevent moisture intrusion and subsequent mold growth. Proper insulation and sealing of windows, doors, and other openings can play a significant role in reducing the risk of mold infestation.
Applying Mold-Resistant Paints or Coatings
Applying mold-resistant paints or coatings to surfaces can provide an additional layer of protection against mold growth. These specialized products contain additives that inhibit the growth of mold and mildew. By using mold-resistant paints or coatings, you can create an environment that is less conducive to mold growth and easier to clean and maintain.
Using Dehumidifiers or Humidity Control Systems
In areas where high humidity is a consistent problem, the use of dehumidifiers or humidity control systems can be beneficial. By controlling and maintaining the relative humidity within an optimal range (usually below 60%), you can effectively prevent mold growth. Dehumidifiers and humidity control systems are particularly useful in basements, crawlspaces, or other areas prone to high humidity.
Clearance Testing and Post-Remediation Verification
Conducting Final Mold Testing
Once the mold remediation process is complete, it is important to conduct final mold testing to ensure the effectiveness of the remediation efforts. This involves collecting air and surface samples from the previously affected areas and analyzing them in a laboratory. By comparing the results to the baseline samples collected during the initial assessment, you can verify that the mold has been successfully removed and the air quality has improved.
Assessing Air Quality
Along with mold testing, assessing the air quality in your house is an essential step in the post-remediation verification process. This can involve monitoring for any unusual odors or signs of moisture and using additional air quality testing methods such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or volatile organic compound (VOC) testing. Assessing the air quality ensures that your house is safe and free from contaminants after the mold remediation process.
Verifying the Effectiveness of Mold Removal
The goal of mold remediation is to effectively remove mold and restore a healthy living environment. Verifying the effectiveness of mold removal involves assessing whether all visible mold has been successfully eliminated and whether the underlying cause of the mold infestation has been addressed. This can be done through visual inspections, moisture readings, and air quality testing. Verification ensures that the mold removal process has been thorough and successful.
Providing Documentation and Certifications
To provide peace of mind and assurance, it is important for mold remediation professionals to provide documentation and certifications to validate their work. This can include detailed reports outlining the steps taken in the remediation process, photographs of the affected areas before and after remediation, as well as any certifications or qualifications held by the professionals involved. Having proper documentation and certifications helps establish trust and confidence in the mold remediation process.

Factors Affecting the Duration of Mold Remediation
Size and Complexity of the Mold Infestation
The size and complexity of the mold infestation can significantly impact the duration of the remediation process. Larger and more widespread mold infestations will require more time and resources to address properly. Additionally, if the mold has spread to hard-to-reach or hidden areas, such as within wall cavities or under flooring, the remediation process may take longer to ensure thorough removal.
Extent of Mold Growth
The extent of mold growth within the affected areas will also affect the duration of the remediation process. Mold that has deeply penetrated materials or has heavily colonized surfaces will require more extensive cleaning and removal efforts. The more mold that needs to be removed, the longer it will take to complete the mold remediation process.
Accessibility of Mold-Infested Areas
The accessibility of mold-infested areas can impact the efficiency and duration of the remediation process. If the mold is located in areas that are difficult to access or require the removal of obstacles, such as furniture or fixtures, the remediation process may take longer. Ensuring proper access to all affected areas and removing any barriers will help expedite the remediation process.
Presence of Hidden Mold
The presence of hidden mold can prolong the duration of the remediation process as it may require additional investigation and testing to locate. Mold that is hidden within wall cavities, behind wallpaper, or under flooring can be challenging to detect and remove. It is important to thoroughly inspect and test for hidden mold to ensure comprehensive remediation.
Type of Mold Present
Different types of mold may require specific remediation methods and treatments, which can impact the duration of the process. Some molds are easier to remove and control, while others may be more stubborn and resistant to treatment. The type of mold present in your house will determine the specific remediation techniques and products needed, which can affect the overall duration of the process.
Availability of Resources and Equipment
The availability of necessary resources and equipment can also affect the duration of the mold remediation process. If there are delays in obtaining the required tools, chemicals, or protective equipment, it may prolong the process. Having access to the appropriate resources and equipment from the start will help ensure a smoother and more efficient mold remediation process.
Professional Expertise and Experience
The expertise and experience of the mold remediation professionals involved can greatly impact the duration of the process. Experienced professionals will be more efficient in identifying, diagnosing, and addressing mold infestations. Their knowledge and skill set allow them to expedite the remediation process while ensuring effective and thorough removal of mold.
Typical Timeframe for Mold Remediation
Small-Scale Mold Infestation (Up to 10 sq. ft.)
For small-scale mold infestations, such as those covering up to 10 square feet, the mold remediation process can typically be completed within a few days. This includes the initial assessment, developing a remediation plan, removal of mold-infested materials, cleaning and disinfecting affected surfaces, and drying the affected areas. Clearance testing and post-remediation verification are also conducted during this timeframe to ensure successful mold removal.
Moderate Mold Problem (10 – 100 sq. ft.)
For moderate mold problems, covering between 10 and 100 square feet, the remediation process may take anywhere from a few days to a week. In addition to the steps involved in small-scale mold infestations, this timeframe allows for more extensive removal and treatment of mold-infested materials. The drying and dehumidifying process may take longer due to the increased area affected.
Extensive Mold Infestation (Over 100 sq. ft.)
Cases of extensive mold infestations, with over 100 square feet affected, will require more time and resources for remediation. The duration for extensive mold infestations can range from several days to a couple of weeks or more. The thorough removal and treatment of mold-infested materials, along with the drying and dehumidifying process, will take longer due to the larger area involved. Professional expertise and experience are vital in successfully addressing extensive mold infestations.
Complicated Mold Remediation Projects
Some mold remediation projects may involve additional complexities, such as multiple levels of a house, intricate building structures, or extensive hidden mold. These complicated projects often require more time for thorough inspection, testing, and removal. The duration for complicated mold remediation projects will depend on the specific challenges and factors involved, and may range from several weeks to months.
In conclusion, the duration of mold remediation depends on several factors such as the size and complexity of the mold infestation, the extent of mold growth, the accessibility of mold-infested areas, the presence of hidden mold, the type of mold present, the availability of resources and equipment, and the expertise and experience of the professionals involved. By following a comprehensive plan and using appropriate remediation techniques, mold can be effectively removed and prevented from recurring in your house.